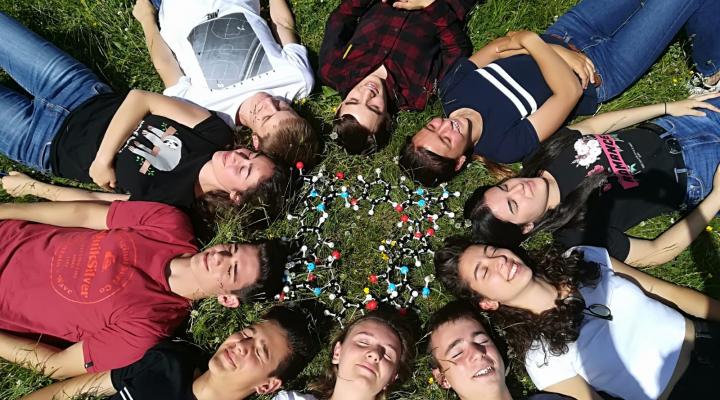

Joves i Ciència
Impulsem les vocacions científiques i tecnològiques de joves estudiants amb gran talent i interès, potenciant el seu entusiasme per la recerca mitjançant un acompanyament intensiu de 3 anys amb experiències singulars i oportunitats en projectes de recerca nacionals i internacionals.












Laboratoire EBI - Université de Poitiers








L'any 2022 va ser declarat com l'Any d'investigació Ramon y Cajal, en commemoració de la personalitat científica més important de la història de l'Estat Espanyol. Durant el 2023, 2024 i 2025 es realitzaran tot tipus d'activitats relacionades amb ciència i recerca.


La Universitat de Cambridge és la segona universitat de parla anglesa més antiga del món, després de la d'Oxford. En el Rànquing de Xangai de 2021 estava classificada la tercera del mon i primera del Regne Unit, per darrere de la Universitat de Harvard i la Universitat de Stanford. Cambridge és la universitat que acumula més receptors del Premi Nobel entre ex-alumnes i professors, fet que la situa en un punt molt alt del rànquing d'universitats.
L'Institut de Recerca de Materials Avançats de la Universitat Jaume I (Institut de Materials Avançats, INAM) és un centre de recerca en ciència i tecnologia interdisciplinària en els camps de la física, la química i àmbits afins, aplicats als materials avançats, amb vocació cap a la progrés de l'entorn socioeconòmic i excel·lència científica amb influència i impacte internacional. L'INAM està orientat a la ciència excel·lent en fonaments i teoria, centrat en les aplicacions. Per tal d'aconseguir innovacions substancials, l'INAM reforçarà la investigació fonamental per entendre i desentranyar els processos bàsics, així com les interaccions físiques i químiques de molècules i materials. Els resultats de naturalesa aplicada es traslladaran al sistema productiu per contribuir a una economia basada en la creativitat i la millora de les condicions de vida. Per tant, l'INAM promourà avenços substancials en les fronteres del coneixement i també donarà suport a noves línies de producció.


L’Autoritat Europea de Seguretat Alimentària (European Food Safety Administration en anglès), s’encarrega de proveir de consell científic i comunicació sobre riscs associats a la cadena alimentària. Va ser fundadada per la Unió Europea i opera independentment de les institucions europees legislativa i executiva i dels estats membres.


Amb més de 25 anys d'història, l'Institut de Recerca d'Intel·ligència Artificial (IIIA), associat Consell Superior de Recerques Científiques (CSIC), és un centre de referència a Espanya i a Europa en l'àmbit de la recerca en Intel·ligència Artificial. Entre les seves línies de treball es troben la modelització i automatització del raonament complex, l'aprenentatge automàtic, els mercats electrònics, la robòtica, i la IA aplicada a la música. D'altra banda, el IIIA desenvolupa les seves recerques compromès amb els Objectius de Desenvolupament Sostenible en el camp de l'educació, la salut, la mobilitat, la indústria i l'ètica, entre altres. A més, el IIIA manté un fort compromís amb la formació de futurs investigadors, havent supervisat més d'un centenar de tesis doctorals des de 1987, i amb la transferència de les aplicacions de la IA a la indústria i a la societat en general.


L’Institut de Recerca de l’Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, creat el 4 de juny de 1992, és una fundació de caire científic que té per missió promoure la recerca bàsica, clínica, epidemiològica i de serveis sanitaris en el camp de les ciències de la salut i la biomedicina, amb el darrer objectiu de contribuir a la millora de la salut de la població. El 10 de desembre de 2003, la Generalitat de Catalunya va aprovar l’adscripció de l’Institut de Recerca de l’Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau com a Institut Universitari de Recerca de la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB).


El Centro de Investigación Cooperativa en Biomateriales (CIC biomaGUNE) es troba a Sant Sebastià i està en funcionament des del desembre de 2006. CIC biomaGUNE és una organització d'investigació sense ànim de lucre creada per a promoure la recerca científica i la innovació tecnològica en els més alts nivells al País Basc seguint la política Bio Basc amb la finalitat de crear un nou sector de negoci basat en les ciències biològiques.


Systematics is a basic biological discipline that investigates and describes the biodiversity on our planet. The science conducted at the Bavarian State Collection involves research on the taxonomy, phylogeny, and natural history of animals, and provides an adequate and sustainable depository for zoological specimens. Zoologische Staatssammlung München (SNSB) is, with almost 22 million zoological objects (labels), one of the largest natural history collections in the world. Many of these specimens have been collected by staff and other collectors during the 200 year long history of the ZSM. One of our main aims is to protect the enormous biological information associated with each zoological object and to make this information available to the scientific and general public.


The Young Brainport Summer School (YBSS) offers room to 40 top talents in the age of 15 to 18 years from all around the world. The participants will get acquainted with the Brainport Eindhoven region in a unique and unforgettable way. Their great interest and passion for science and technology will be encouraged by demonstrating the most advanced technological research and world class applications of our region. Combined with a good mixture of social activities with talented peers, YBSS is “a life-changing experience”. The Brainport Eindhoven Region is a vibrant and highly innovative region existing of 21 municipalities located in the Southeast of the Netherlands. Brainport, with Eindhoven at its heart, plays a decisive role as one of the key cornerstones of the Dutch economy. As an innovative top technology region, Brainport defines the competitiveness of the Netherlands. Its strength lies in the combination of high-tech, design and a unique model of collaboration in which opportunities that are generated by the rapidly changing world around us are seized. A culture of open innovation predominates: partners from all disciplines collaborate, share and multiply knowledge. Those with a scientific background work together with market researchers, designers, sociologists and psychologists thereby boosting economic growth and contributing to a sustainable, healthy, safe and secure society.


XLAB - International Science Camp is an experimental laboratory for young people and bridges the gap between high school and university. XLAB offers ambitious practical experiments and courses in biology, chemistry, physics and computer science supervised by scientists of the University of Göttingen. XLAB collaborates with scientific institutes of the university, the research institutes of the Max Planck Society, the Laser Laboratory and the German Primate Center.


Fundada por Stephen Wolfram en 1987, Wolfram Research es una de las compañías más respetadas en computación, web y software para la nube del mundo; así como una potencia de la innovación científica y técnica. Como pionera en ciencias de la computación y el paradigma computacional, nosotros hemos mantenido una visión a largo plazo para desarrollar ciencia, tecnología y herramientas para hacer de la computación una fuerza cada vez más potente en el mundo de hoy y del mañana.


Studying at the University of Twente is different than studying anywhere else. Why? Because our vision of the world you will live and work in after leaving us has led us to develop a distinct view on education and research – and on the kind of scientists, engineers and professionals tomorrow’s world will need.


The Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) Heidelberg aims to study organismic biology beyond the borders of organisational level. Research and teaching at COS is dedicated to study organismic biology from the basic molecular principles to cell biology, developmental biology and physiology both in plants and in animals and to further extend into evolution, biodiversity, systems biology and biotechnology.


The University of Georgia, a land-grant and sea-grant university with statewide commitments and responsibilities, is the state’s oldest, most comprehensive, and most diversified institution of higher education. Its motto, “to teach, to serve, and to inquire into the nature of things,” reflects the University’s integral and unique role in the conservation and enhancement of the state’s and nation’s intellectual, cultural, and environmental heritage.


The University of Cambridge's mission is to contribute to society through the pursuit of education, learning and research at the highest international levels of excellence. The University is a confederation of Departments, Schools, Faculties and Colleges.


The Texas Mathworks Honors Summer Math Camp (HSMC) is an intensive summer program for outstanding high school students who are excited about doing mathematics. The goal of the program is to develop talented youth of all backgrounds by an immersive and in-depth experience in a unique learning environment. Students develop important skills for future degrees and careers in math, science, engineering, and many other fields.


Teesside University is a public university with its main campus in Middlesbrough that has the ambition to be an international university at the heart of the Tees Valley with a reputation for academic excellence. It is founded on a rich heritage, which has influenced its development into the dynamic, energetic and innovative institution it is today. Teesside University generates and applies knowledge that contributes to the economic, social and cultural success of students, partners and the communities they serve. Through education enriched by research, innovation, and engagement with business and the professions, they transform lives and economies. The University consists of six schools: Design, Culture and the Arts; Computing; Health and Social Care; Science and Engineering; Social Science, Business and Law; and Teeside University Business School.


The Summer Science Program (SSP) is a 39-day residential enrichment program in which gifted high school students from around the world complete a challenging, hands-on research project in celestial mechanics. There are two research projects on three campuses: SSP in in Astrophysics at New Mexico Tech and University of Colorado Boulder, and the SSP in Biochemistry at Purdue University and University of California San Diego.

Summer School of Science (S3/S3++) is a unique place where like-minded individuals of all ages get together to share their enthusiasm for knowledge and discovery. Around 30 students from all over the world participate each year in this adventure that combines passionate work and learning with opportunities to make life-long friendships.


School of Molecular and Theoretical Biology (SMTB) offers a chance to work on a real scientific question alongside real scientists with a possibility of obtaining real and novel results. Within a wide diversity of topics in the natural sciences and mathematics SMTB is focused on molecular and theoretical biology. You will hear lectures, learn how to perform different techniques and calculations and explore current ideas in areas of molecular and theoretical biology.


The Ross Program at the Ohio State University is an intensive summer experience designed to encourage motivated pre-college students to explore mathematics. During six weeks, students are immersed in a world of mathematical discovery. The central goal of the Ross Program is to instruct bright young students in the art of mathematical thinking and to inspire them to discover for themselves that abstract ideas are valuable and important. First year participants take the basic course in number theory. For most students, this is the first time they are asked to consider entirely new questions, to develop methods that they have not seen before, and to justify every answer. The value of a mathematics education lies not only in obtaining proficiency in computational tasks, but also in building a foundation for critical thinking. Students who have never asked why things work the way they do are not prepared to lead the way to future scientific innovation. It is precisely this independence of thought and questioning attitude that the Ross Program strives to nurture.


Rosetta Institute of Biomedical Research is an independently funded medical research institute founded by Dr. Ryan Holzer, PhD. The institute is funded by internally generated revenue, and by private donations. We conduct basic and translational research on apoptosis in multiple myeloma and other malignancies, with the ultimate goal of identifying novel driver mutations responsible for tumorigenesis and the emergence of chemoresistant clones. Current research projects include: 1) discovering novel mechanisms of bortezomib (Velcade) resistance in multiple myeloma, 2) characterizing pro-apoptotic signaling pathways activated by Type 1 interferon (IFN-α/β), 3) the identification and characterization of ubiquitin ligases that regulate cell survival, 4) transcriptomic analysis and miRNA profiling of clonal evolution in cancer, 5) the discovery of novel roles for IL-6 family cytokines in hematologic malignancies, 6) The identification of novel alternatively spliced transcripts that contribute to tumor progression and the RNA-binding proteins that regulate rare exon inclusion/exclusion, 7) the role and regulation of autophagy during proteotoxic stress, 8) adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mechanisms of ER stress-induced apoptosis, 9) the identification and characterization of the multiple myeloma stem cell compartment and the bortezomib-resistant subclone, 10) The role of hypoxia in drug sensitivity and clonal evolution. A variety of techniques are being used at the Institute to address these questions, including bioinformatic analyses, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, tissue culture and mouse models of cancer. Ultimately this knowledge will be translated into next generation therapeutics for the treatment of cancer and other diseases associated with splicing errors or disturbances in proteostasis.


The Rockefeller University Summer Science Research Program (SSRP) provides high school students with a unique and personalized opportunity to conduct hands-on research under the mentorship of leading scientists at one of the world's premier biomedical research facilities. During this rigorous 7-week program, SSRP students become immersed in scientific culture while gaining an appreciation for the process of biomedical discovery. Through a combination of laboratory experimentation, interactive lectures, and dynamic coursework, students will learn fundamental research techniques, become better acquainted with scientific peer-reviewed literature, and improve critical thinking. Equally as important, students will have a lot of fun -- we strive to make the SSRP an inclusive and supportive environment where every student’s voice is heard and respected. Please see the Description of Coursework (link is external) to read about the classes that supplement the in-lab experience. See Examples of Laboratory Projects (link is external) to read about some of the past projects undertaken by SSRP students.


Program in Mathematics for Young Scientists (PROMYS) is a six-week summer program at Boston University designed to encourage strongly motivated high school students to explore in depth the creative world of mathematics in a supportive community of peers, counselors, research mathematicians, and visiting scientists. Each year, PROMYS and the Clay Mathematics Institute (CMI) offer advanced seminars for returning PROMYS students. Returning students also engage in original research under the mentorship of professional mathematicians. Counselors and returning students will also organize their own seminars.


Petnica Science Center is the biggest and the oldest independent nonprofit organization for extracurricular, informal science education in South Eastern Europe. Since 1982, Petnica has organized more than 2,500 programs for nearly 50,000 students and science teachers in 15 disciplines of science, technology and humanities. Summers in Petnica Science Center are the busiest and most engaging part of our year-long course plan. Students realize their projects and take part in various forms of field work (archaeological excavations, collecting biological samples, etc.).


Chemistry at Newcastle has a long history of pushing back scientific boundaries and providing an excellent environment in which to, work, study and conduct research. The School of Chemistry is currently home to over 80 members of staff and over 350 students, all of who work together to ensure a vibrant community in which everyone can reach their full potential.


The Music Technology Group (MTG) of the Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) in Barcelona, part of its Department of Information and Communication Technologies, carries out research on topics such as audio signal processing, music information retrieval, musical interfaces, and computational musicology. The MTG wants to contribute to the improvement of the information and communication technologies related to sound and music, carrying out competitive research at the international level and at the same time transferring its results to society. To that goal, the MTG aims at finding a balance between basic and applied research while promoting interdisciplinary approaches that incorporate knowledge and methodologies from both scientific/technological and humanistic/artistic disciplines.


Research at the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics concentrates on the interaction of light and matter under extreme conditions. One focus is the high-precision spectroscopy of hydrogen. In the course of these measurements Prof. Theodor W. Hänsch developed the frequency comb technique for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 2005. Other experiments aim at capturing single atoms and photons and letting them interact in a controlled way, thus paving the way towards future quantum computers. Theorists on the other hand are working on strategies to communicate quantum information in a most efficient way. They develop algorithms that allow the safe encryption of secret information. MPQ scientists also investigate the bizarre properties quantum-mechanical many-body systems can take on at extremely low temperatures (about one millionth Kelvin above zero). Finally light flashes with the incredibly short duration of several attoseconds (1 as is a billionth of a billionth of a second) are generated which make it possible, for example, to observe quantum-mechanical processes in atoms such as the 'tunnelling' of electrons or atomic transitions in real time.


The Center for Excellence in Education nurtures careers of excellence and leadership in science and technology for academically talented high school and college students. CEE is dedicated to encouraging international understanding between and among future leaders of the world


London International Youth Science Forum (LIYSF) is a two week residential event in London, with lectures and demonstrations from leading scientists, visits to industrial sites, research centers, scientific institutions and organizations, including world class laboratories and universities. LIYSF attracts over 500 of the world’s leading young scientists aged 16-21 years old from more than 70 participating countries.


El Laboratoire de Physique Nucléaire et d'Hautes Energies de la Sorbonne Université és una unitat de recerca conjunta de l’Institut Nacional de Física Nuclear i Física de Partícules, el Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS) i de les universitats Pierre i Marie Curie i Paris Diderot. El laboratori es dedica a diversos grans programes experimentals sobre física de partícules, astropartícules i cosmologia, realitzats en el marc de col·laboracions internacionals amb infraestructures de recerca de tot el món, centres d’acceleradors de partícules i observatoris.


LAM is one of the largest astrophysics public research institutes in France. It combines fundamental research in Astrophysics and the development of instrumentation for space and ground-based telescopes


The Laboratoire d’astrophysique de Bordeaux (LAB) is a joint research unit (UMR) between the University of Bordeaux (UB) and the National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS). It is part of the Observatoire des Sciences de l’Univers (OASU), itself an internal school of the Science and Technology Department of the UB and observatory of the sciences of the Universe (OSU) of the Institut national des sciences de l’Univers (INSU) of CNRS.


International Summer Science Institute (ISSI) is an integrated science program that is geared toward talented, highly-motivated science students who have demonstrated their motivation to gain deeper scientific knowledge above and beyond what is taught in high school and who are interested in pursuing a career in research science. The main focus of the program is student participation in the on-going laboratory work of the Weizmann Institute of Science.


Perimeter Institute is a leading centre for scientific research, training and educational outreach in foundational theoretical physics. Founded in 1999 in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, its mission is to advance our understanding of the universe at the most fundamental level, stimulating the breakthroughs that could transform our future. Perimeter also trains the next generation of physicists through innovative programs, and shares the excitement and wonder of science with students, teachers and the general public.


The International Astronomical Youth Camp (IAYC) is a three-week long summer camp aiming to promote knowledge of astronomy and astronomy related sciences in a unique international atmosphere. Every year the IAYC takes place somewhere in Europe. About seventy people from a wide range of different countries live together for three weeks


L’Institut de Recerca en Biologia d’Insectes (IRBI) és una unitat de recerca conjunta de la Universitat de Tours i el CNRS que es dedica a l’anàlisi de processos adaptatius i evolutius a tots els nivells d’organització, des del genoma fins a les comunitats. La investigació es basa en mètodes i conceptes d’ecologia, morfologia funcional, genètica i biologia evolutiva. Els seus estudis es caracteritzen pels models utilitzats, els insectes i un enfocament integrador dels problemes tractats, gràcies a la diversitat d’habilitats i xarxes col·laboratives dels seus investigadors/es.


The Research Group on Image Processing (GPI) of the Univerity Pompeu Fabra (UPF) in Barcelona focuses on the development of models and algorithms for image processing and computer vision. The main research lines are: 3D reconstruction and view synthesis for sport events and 3D Television and cinema, development of tools for digital video post-production, object identification including logo detection, color image processing and digital photography, variational models for image processing and computer vision, and applied Mathematics: geometric partial differential equations.


HCSSiM is an intensive six-week summer program for mathematically talented high school students that is both demanding and expanding. Participants are expected to spend a major portion of each day actively engaged in learning, doing, and sharing mathematics. The daily schedule includes 4 hours of morning classes (Monday-Saturday), the Prime Time Theorem in the afternoon, and problem sessions in the evening. Afternoons are devoted to reading, rest, recreation, occasional trips to town and informal study. Participants have unparalleled access to faculty members in classrooms, at meals, and in the program dorm. Productive collaborations continue long after the program, and many lifelong friendships are forged.


Environmental Studies Summer Youth Institute (ESSYI) at Hobart and William Smith Colleges provides exceptional opportunities to explore the scientific, social, and humanistic perspectives of environmental issues. The Institute offers a two-week, college-level interdisciplinary program for talented high-school students entering their junior and senior years. The program is designed as an introduction to a variety of environmental issues and perspectives on nature and environment.


TU Delft is a university with a leading global reputation. We would like to welcome you at our campus, to experience our full range of high-quality disciplines, courses and unique facilities. The TU Delft is actively engaged in partnering with peer universities, research institutions and government agencies across the globe in order to facilitate a wide variety of intellectual interactions and exchanges. Feel free to explore the TU Delft as part of a delegation or student


Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto (CAUP) is a private non-profit scientific institution of the University of Porto, officially recognized as institution of public utility. It started its activities in 1990, and its stated objective is to support and promote Astronomy through frontline research, training at the post-graduate and undergraduate levels, activities for primary and high schools, science outreach and popularization of scientific culture. CAUP is unique in that it shares its space with a Planetarium (run by a dedicated outreach unit), and CAUP researchers are supposed to devote 5% of their time to help with those outreach activities.


The Centre for Climate Change (C3), set up in late 2008 at the Campus de les Terres de l'Ebre by the University Rovira i Virgili (Tarragona, Spain), is focused on researching, outreaching and knowledge transferring in the fields of climate reconstruction and analysis. The specific activities include high-quality climate datasets development (comprising data rescue procedures and research on homogenization methods) and climate variability and change assessments (particularly climate change detection) at different spatial (from local to global) and temporal (from sub-daily to annual) scales.


Imperial College London is a world top ten university with an international reputation for excellence in teaching and research.


The Sainsbury Laboratory (TSL), a Norwich (Regne Unit), és un institut de recerca líder al món en investigació biològica fonamental en les interaccions de plantes i microbis i en el desenvolupament de tecnologies per a l’aplicació en malalties de plantes, resistència a malalties i simbiosis microbianes en plantes.


La Universitat d’Oxford, ubicada a Oxford (Regne Unit), és una de les universitats de recerca més prestigioses del món constituïda per varies institucions, 38 colleges i un ampli ventall de departaments acadèmics. La Universitat d’Oxford ha educat molts alumnes destacats, incloent 69 guanyadors del premi Novel, 27 primers ministres del Regne Unit, caps d’estat i de govern de tot el món, 3 medalles Fields i 6 guanyadors del Premi Turing.


The John Innes Centre is an independent, international centre of excellence in plant science, genetics and microbiology.


The Laboratoire d’astrophysique de Bordeaux (LAB) is a joint research unit (UMR) between the University of Bordeaux (UB) and the National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS). It is part of the Observatoire des Sciences de l’Univers (OASU), itself an internal school of the Science and Technology Department of the UB and observatory of the sciences of the Universe (OSU) of the Institut national des sciences de l’Univers (INSU) of CNRS.


We are a community where you can be an individual and achieve exceptional things. We are committed to learning and exploration, to discovery and impact.
www.wustl.edu


The University of Eastern Finland is one of the largest universities in Finland. We show courage in crossing academic boundaries and our interdisciplinary approach is internationally recognised.Our research is ranked among the best in the world in several fields. As a multidisciplinary university, we train experts for the various sectors of society. We seek solutions to global challenges through multidisciplinary research and education. In collaboration with our partners, we generate new knowledge, expertise and innovations.


La Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM) és una institució de llarga trajectòria i ampli reconeixement social que aspira a situar-se entre les primeres universitats d'Europa i a consolidar-se com a centre de referència per al continent llatinoamericà. El Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) la sitúa entre les posicions 4 i 9 i el QS World University Ranking li otorga la posició 4 a nivell nacional.


El Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) es un centro de investigación español internacionalizado y seleccionado por el Gobierno español como "Centro de Excelencia Severo Ochoa"
La Ruta de las Estrellas es un proyecto con el objectivo de despertar vocaciones científicas en astronomia en jóvenes estudiantes. Fue creada en el año 2004 por la Asociación Shelios. Las Expediciones Científicas de Shelios y el proyecto europeo STARS4ALL ponen al servicio de los jóvenes estudiantes las herramientas capaces de despertar pasión por la ciencia. La Ruta de las Estrellas acompaña y tutela los primeros pasos por el Universo de la Investigación. Investigar, emprender, participar y convivir es la fórmula empleada para comenzar el viaje hacia el conocimiento; es una ruta inolvidable, para toda la vida.


Vall d’Hebron Institut de Recerca (VHIR) és una institució del sector públic que promou i desenvolupa la investigació i la innovació biosanitària de l’Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, estant orientada a trobar solucions als problemes de salut de la ciutadania. Té la voluntat de contribuir al desenvolupament científic, docent, social i econòmic del seu àmbit de competència.


El Vall d’Hebron Institut de Recerca (VHIO) és un destacat centre oncològic integral d'excel·lència on els científics i doctors adopten un model d'investigació purament traslacional, treballant conjuntament en equips multidisciplinaris per accelerar i avançar en el camp de les teràpies personalitzades i específiques contra el càncer.


La Salle és una institució amb més de 300 anys d’història i amb una àmplia presència internacional. Pioners en oferir estudis que s’adapten en cada moment a les necessitats del mercat i la societat.


El Departament de Tecnologies de la Informació i les Comunicacions (DTIC) de la Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) és la seu dels docents i investigadors en el camp de les tecnologies de la informació i les comunicacions, el qual agrupa les disciplines de telecomunicacions i de ciències de la computació. A través de l'Escola Politècnica de la UPF (ESUP), el DTIC acull els graus en Enginyeria Telemàtica, Enginyeria de Sistemes Audiovisuals i Enginyeria en Informàtica. Les activitats de recerca del DTIC estan organitzades al voltant de quinze grups, que desenvolupen una àmplia gamma de temes, en els quals s'inclouen el networking, les comunicacions wireless, el multimèdia, el processament de la imatge i la música, la imatge mèdica, les tecnologies interactives, la intel·ligència artificial, el data mining i la neurociència computacional, entre d'altres. El departament participa activament en programes de recerca nacionals i europeus, i té acords de cooperació activa amb altres importants universitats i empreses.


L'Institut de Tècniques Energètiques (INTE) és un institut de recerca de la Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC) les funcions principals del qual són la recerca i la transferència de tecnologia, organitzades en quatre programes que comprenen àrees d'especialització en radiacions ionitzants, tecnologies de producció de l'hidrogen i desenvolupament de materials per a aplicacions energètiques, termohidràulica, física amb neutrons i acceleradors de partícules.


La Facultat de Matemàtiques i Estadística, creada el setembre de 1992 Són els estudis de matemàtiques triats pels estudiants de secundària amb millor expedient acadèmic: els únics a l'estat espanyol que mantenen any rere any una demanda superior a l'oferta.


El campus de l’ETSEA de la Universitat de Lleida és el principal campus agroalimentari, forestal i veterinari de Catalunya i un dels principals d’Espanya. Es va crear el 1972 amb els estudis d’Enginyeria Tècnica Agrícola


El Departament d’Enginyeria Agroforestal està especialitzat en les diferents àrees de coneixement relacionades amb l’aplicació de l’enginyeria al món agrari, al món forestal i a la construcció. El departament centra la seva activitat docent i de recerca en dos campus de la Universitat de Lleida: el Campus de l’ETSEA (Escola Tècnica Superior d’Enginyeria Agrària) i el Campus de Cappont-EPS (Escola Politècnica Superior). La seu del Departament d’Enginyeria Agroforestal es troba al campus ETSEA on hi ha la direcció i la secretaria del departament.


Driven by intellectual creativity and critical thinking since 1479, researchers and students at the University of Copenhagen have expanded horizons and contributed to moving the world forward. With its 5,000 researchers and 39,000 students, the University boasts an international research and study environment and is highly ranked on the leading ranking lists of the world's best universities.
La UB és la principal universitat pública de Catalunya, la que té un nombre més gran d’estudiants i l’oferta formativa més àmplia i completa. A més, és el principal centre de recerca universitari de l’Estat i un dels més importants d’Europa, tant pel nombre de programes de recerca com per l’excel·lència assolida en aquest terreny.


MathCamp és un programa que organitza la Fundació Talento Matemático y Científico que inclou escoles i residències de matemàtiques, ciències, robòtica i anglès per a escolars, tant a Espanya com a nivell internacional. Es tracta d'una escola d'habilitats en anglès, matemàtiques i ciències, per a estudiants de primària i secundària.


L'Institut de Salut Global de Barcelona (ISGlobal) és el fruit d'una aliança innovadora entre "la Caixa" i institucions acadèmiques i governamentals per contribuir a l'esforç de la comunitat internacional amb l'objectiu d'afrontar els reptes de la salut en un món globalitzat. ISGlobal consolida un node d'excel·lència basat en la recerca que té el seu origen en els àmbits hospitalari (Hospital Clínic i Parc de Salut MAR) i acadèmic (Universitat de Barcelona i Universitat Pompeu Fabra) i que en el camp de la salut global acumula més de 30 anys d'experiència. El seu model de treball aposta per la translació del coneixement generat per la ciència a través de les àrees de Formació i Anàlisi i Desenvolupament Global. La meta darrera dels projectes que constitueixen l'agenda d'ISGlobal és corregir les desigualtats a l'estat de salut de les diverses poblacions del món.


L’Institut Investigació Biomèdica Barcelona Sant Pau (IBBSP) de l’Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, creat el 4 de juny de 1992, és una fundació privada de caire científic que té per missió promoure la recerca bàsica, clínica, epidemiològica i de serveis sanitaris en el camp de les ciències de la salut i la biomedicina, amb el darrer objectiu de contribuir a la millora de la salut de la població.


El Grup de Recerca en Insuficiència i Regeneració Cardíaca (ICREC) del Servei de Cardiologia de l’Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, forma part de l'Institut d'Investigació en Ciències de la Salut Germans Trias i Pujol (IGTP). Treballa activament des de 2002 fent recerca translacional sobre la recuperació de la funció cardíaca. Ha participat en experiments pioners sobre quimerisme i microquimerisme en el cor humà i té molta experiència en cultius cel·lulars de cèl·lules mare endotelials circulants, cèl·lules mesenquimals de moll d’os i cèl·lules mare de teixit adipós epicardiac i subcutani. També està implicat en projectes d’ enginyeria tissular amb polímers biocompatibles per a desenvolupar estructures bioactives amb aplicacions biomèdiques. I en la recerca de nous biomarcadors diagnòstics i pronòstics de la Insuficiència cardíaca.


L'Institut de Recerca Biomèdica de Lleida Fundació Dr. Pifarré (IRBLleida) es constitueix amb la finalitat de crear sinergies entre la recerca bàsica, la recerca clínica i la investigació epidemiològica, perquè la investigació biomèdica sigui el motor de la millora de la pràctica clínica diària, en benefici de tota la població. És a dir, abasta una cadena de recerca translacional, des de la investigació bàsica, orientada a la comprensió dels mecanismes fisiològics i patològics de l'organisme humà, fins a la investigació que estudia el comportament de les malalties en grans grups poblacionals.


The Institute of Computational Chemistry and Catalysis (IQCC) of the University of Girona (UdG) is a worldwide reference unit in computational chemistry and catalysis that aims at carrying out groundbreaking research on predictive chemistry for catalysis, with special focus on the processes occurring at the confined space for the coming years. The unit was created as Institute of Computational Chemistry (IQC) in 1993, and its rules were approved in 1997 by the Senate of the UdG. In 2012, the IQC was joined by two experimental research groups, the Bioinorganic and Supramolecular Chemistry (QBIS) and Transition Metals in Organic Synthesis (METSO) groups, and changed its name to IQCC (approved by UdG Senate in February 2013). This was motivated by a previous history of collaborations and synergies between the three research groups. With this transformation, the IQCC wants to face the new challenges in research and adapt to the new research frame at the Catalan, Spanish, and European levels


L’Institut de Química Avançada de Catalunya (IQAC)és un dels centres d’investigació del Consell Superior d’Investigacions Científiques (CSIC). L’Institut es troba a Barcelona i va ser creat l’any 2007 amb la missió de realitzar investigacions d’excel·lència en Ciències Químiques amb l’objectiu general de millorar la qualitat de vida. L’estratègia general per aconseguir aquesta missió implica l’aplicació d’enfocaments químics per abordar i resoldre els desafiaments socials, principalment els relacionats amb la salut humana, la sostenibilitat dels processos i productes químics, i les necessitats de nous materials per a diferents aplicacions. Des de la seva creació, l’IQAC ha mantingut una disposició permanent per transferir els seus resultats i tecnologia al sector industrial.


L’Institut pertany a l’àrea de Recursos Naturals del Consell Superior d’Investigacions Científiques (CSIC) i és el centre més gran de recerca marina d'Espanya i un dels més importants de la regió Mediterrània. Es dedica íntegrament a l’estudi de mars i oceans. La seva recerca busca aprofundir i avançar en el coneixement científic i esbrinar quin paper tenen els oceans en el context del planeta.


Centre ValBio works to protect Madagascar’s unique and biologically diverse ecosystems through conservation science and projects that directly benefit the local people, including rural health care delivery. CVB has a world-class research station sited on the edge of Madagascar's beautiful and abundant Ranomafana National Park. Under the direction of world-renowned primatologist Patricia Wright, Centre ValBio facilitates hands-on science to sustain the resources and people of Madagascar. In collaboration with villagers, we're expanding the frontiers of knowledge while safeguarding biodiversity for future generations.


L'Institut de Ciència i Tecnologia Ambientals (ICTA-UAB) és un centre multidisciplinari que promou la investigació i la formació de postgrau en ciències ambientals. La finalitat és millorar la comprensió del canvi ambiental global, i de la naturalesa i les causes dels problemes ambientals. A més, estudia les polítiques, estratègies i tecnologies que fomentaran la transició cap a una economia sostenible.


L’Institut de Biologia Evolutiva (IBE) és un centre de recerca mixt de la Universitat Pompeu Fabra (UPF) i el Consell Superior d’Investigacions Científiques (CSIC) fundat l’any 2008. La recerca de l’IBE se centra en els processos i els mecanismes que generen la biodiversitat, i entre els temes que s’hi estudien hi ha l’evolució genètica i molecular, la biologia de les poblacions, la biologia de sistemes complexos i la recuperació de l’ADN antic. L’IBE és l’únic centre de recerca de Catalunya i de la resta de l’Estat que es dedica íntegrament a la biologia evolutiva, i és un referent en aquest camp al sud d’Europa. A l’IBE hi treballen unes cent trenta persones, distribuïdes en els edificis veïns del Parc de Recerca Biomèdica (PRBB) i el del Centre Mediterrani d’Investigacions Científiques (CMIMA).


L'Institut de Recerca Germans Trias i Pujol (IGTP) és un centre de recerca públic situat a Badalona (Barcelonès) que té com a objectiu principal incrementar el coneixement científic per transformar-lo a continuació en una millor salut i atenció mèdica dels pacients i de la comunitat. L'Institut està associat a un dels grans hospitals docents de l'àrea de Barcelona: l'Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol (HUGTP) i forma part del campus biomèdic de Can Ruti. A més, és un centre CERCA i un membre del Bioclúster recolzat i supervisat pel Govern de Catalunya. També està acreditat com a centre d'excel·lència per l'Institut Carlos III i és per tant, l'encarregat de coordinar la investigació científica del campus, treballant en estreta col·laboració amb els altres centres que s'hi ubiquen.


L'Institut d'Investigació Biomèdica de Girona (IdIBGI) és un centre de recerca de la xarxa de centres CERCA de la Generalitat de Catalunya que pretén vertebrar i desenvolupar la recerca de qualitat en ciències biomèdiques i de la salut pública i comunitària i promou la seva translació a la pràctica habitual. Tot amb l’objectiu de respondre als problemes de salut de la població. L’ IDIBGI està estructurat amb grups de recerca de l’ Hospital Universitari Dr. Josep Trueta de Girona (HJT) i de la Universitat de Girona, l’ Institut de Diagnòstic per la Imatge (IDI), l’ Institut Català d’ Oncologia (ICO) i l’ Institut d’ Atenció Primària (IAP) / Institut Català de la Salut a Girona.


L’Institut Català de Recerca de l’Aigua (ICRA) és un referent internacional que aposta per la investigació del cicle integral de l’aigua, en matèria de recursos hídrics, qualitat de l’aigua, en el sentit més ampli de la paraula, (química, microbiològica, ecològica, etc...) i tecnologies de tractament i d’avaluació i la transferència d'aquest coneixement a la societat i al teixit empresarial i industrial. La recerca que es fa a l’ICRA està relacionada amb tots els aspectes relacionats amb l’aigua, en especial aquells que tenen a veure amb el seu ús racional i els efectes de l’activitat humana sobre els recursos hídrics. L’ICRA s’interessa en particular per investigar i resoldre els impactes de la sequera, així com els aspectes de qualitat en el tractament i reutilització d’aigües, dedicant una atenció preferent a la Mediterrània.


The Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES) is a transdisciplinary institution that promotes advanced research, education and knowledge transfer, and social engagement with science. Therefore, we cross and combine different fields of science, humanities and social sciences, but also geosciences and biosciences to apply them to the study of human and social evolution. Our aim is to promote knowledge both about ancient human species of the past and about human beings today. The IPHES was created in December 2004 as a non-profit foundation through an initiative of the Catalan Government, Rovira i Virgili University (URV) and the City of Tarragona.


L'Institut Català d'Oncologia (ICO) és un centre públic i monogràfic sobre el càncer. S'ocupa de la malaltia de manera integral ja que aplega, dins de la mateixa organització, la prevenció, l'assistència, la formació especialitzada i la recerca. L'ICO és una empresa pública creada el 1995 pel Departament de Salut de la Generalitat de Catalunya, que comença a funcionar un any més tard a les instal·lacions de l'Hospital Duran i Reynals de l'Hospitalet de Llobregat. Set anys després, el 2002, s'inaugura l'ICO Girona, a l'Hospital Doctor Josep Trueta, i l'any següent l'ICO Badalona, a l'Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol. El 2014 es posa en marxa l'ICO Camp de Tarragona i Terres de l'Ebre a l'Hospital Joan XXIII de Tarragona i al Verge de la Cinta de Tortosa. Actualment l'ICO és el centre oncològic de referència per a més del 40% de la població adulta de Catalunya.
The Event LAB (Experimental Virtual Environments for Neuroscience and Technology) is at the interface between computer science, psychology and neuroscience. We carry out technical research on virtual environments, with applications to research questions in cognitive neuroscience and psychology. Our special interest is the brain's body representation and the consequences of body ownership. The institutions participating in the Event LAB are University of Barcelona (UB), August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) and Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA).


El Centre de Ciència i Tecnologia Forestal de Catalunya (CTFC), amb seu a Solsona (Lleida), es va constituir inicialment entre el Consell Comarcal del Solsonès i la Universitat de Lleida l'any 1996, i posteriorment, s'hi van incorporar la Diputació de Lleida, la Fundació Catalana per a la Recerca i la Innovació, la Generalitat de Catalunya, la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, la Diputació de Barcelona i l'Ajuntament de Solsona. El CTFC és un consorci públic adscrit a l’Administració de la Generalitat de Catalunya i s’hi relaciona mitjançant el Departament competent en matèria de boscos. També forma part dels centres de recerca de Catalunya (CERCA) i està acreditat com agent TECNIO per la Generalitat (desenvolupador de tecnologia públic). La missió del CTFC és contribuir a la modernització i a la competitivitat del sector forestal, al desenvolupament rural i la gestió sostenible del medi natural, per mitjà de l’excel·lència en recerca i de la transferència de coneixement i de tecnologia a la societat amb l’ànim d’esdevenir un centre de referència en l’àmbit nacional i internacional.


El Centre de Visió per Computador (CVC) és una institució sense ànim de lucre líder en recerca i desenvolupament en el seu camp. Va ser fundat l’any 1995 per la Generalitat de Catalunya i la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), amb la finalitat de fer una investigació d’excel·lència mitjançant la generació de coneixement de qualitat i la transferència de tecnologia cap a la societat oferint, alhora, valor afegit a las empreses. Està format per més de 130 investigadors i especialistes de tot el món. La visió per computador és una tecnologia horitzontal amb diverses aplicacions a biomedicina, mobilitat, seguretat, producció, societat, media... Les seves activitats se centren en la investigació de frontera, en la transferència de tecnologia i la formació. Les línees estratègiques que defineixen la missió del centre es resumeixen en un model que combina talent científic i tecnològic per afavorir el flux entre investigació bàsica i la transferència del coneixement cap a la societat.


The Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) is an international biomedical research institute of excellence, created in December 2000. It is a non-profit foundation funded by the Catalan Government through the Departments of Business & Knowledge, the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation & Universities, the "la Caixa" Banking Foundation, and includes the participation of Pompeu Fabra University. The mission of the CRG is to discover and advance knowledge for the benefit of society, public health and economic prosperity. The CRG believes that the medicine of the future depends on the groundbreaking science of today. This requires an interdisciplinary scientific team focused on understanding the complexity of life from the genome to the cell to a whole organism and its interaction with the environment, offering an integrated view of genetic diseases.


El Centre de Recerca en Agrigenòmica (CRAG) és un consorci públic format pel Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), l'Institut de Recerca i Tecnologia Agroalimentàries (IRTA), la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB), la Universitat de Barcelona (UB) i rep el suport de la Generalitat de Catalunya a través de la Direcció General de Recerca. És un centre de recerca multidisciplinari dedicat a la investigació dels factors genètics que determinen caràcters d’interès en plantes i animals de granja. Fa recerca bàsica amb els criteris de ciència d'excel·lència i recerca d’interès per la millora d'espècies vegetals i animals d'ús en el entorn agroalimentari.


Després de l'aprovació de la nova llei de reproducció assistida (novembre 2003) es va fer possible investigar a Espanya amb embrions humans congelats i amb les cèl·lules mare derivades dels mateixos. El Ministeri de Sanitat i Consum (ara Ministeri de Sanitat, Serveis Socials i Igualtat) va aprovar la creació del Centre de Medicina Regenerativa de Barcelona el mes de juliol de 2004. El CMRB té la missió bàsica d'investigar amb cèl·lules mare pluripotents humanes (embrionàries i induïdes o iPSC), asixí com en diferents models animals per a investigar la regeneració de teixits i òrgans i treballar per a que aquests avenços puguin traslladar-se aviat a la clínica. També s'usen les cèl·lules mare per al modelatge de malalties en la recerca de fàrmacs eficients.


El Centre d’Estudis Avançats de Blanes (CEAB) és un centre del Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC). Aspira a ser un centre amb reputació internacional que sigui referent nacional en Biologia Marina, Limnologia i Ecologia. Focalitza la seva recerca en identificar la diversitat d’organismes, entendre les seves funcions i interaccions amb la natura, així com l’aplicació d’aquest coneixement en l’ús i gestió racional dels recursos del planeta, i la predicció de respostes a modificacions ambientals. Els seus estudis abarquen des de la composició bioquímica i genética dels organismes fins a l’estructura i dinámica de poblacions i ecosistemes. La seva recerca sòlida, actualitzada i creativa pretén fer front als reptes que es plantegen en el desenvolupament d’una societat sostenible.


Barcelona International Youth Science Challenge (BIYSC) is a two-week residential program held annually in the Mediterranean capital which involves 120 young scientists aged between 16 and 18 years old from all over the world. The program was founded with the aim to stimulate scientific talent among high school students and encourage their enthusiasm to pursue scientific research and careers in science. BIYSC covers a broad range of subjects across STEM fields. Different scientific and technological challenges are posed by international research centers based in Catalonia. Participants will have the chance to choose a project that suits their interests and conduct a hands-on and cutting-edge research.


AstroCamp is a joint academic program of the Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto (CAUP) and other institutions in the field of astronomy and physics held in the Centro de Educação e Interpretação Ambiental (CEIA) in Portugal. It provides participants with high-level and inspiring training, rest and recreation in a secluded and tranquil setting away from the stresses of urban centers. The program is intended for secondary school students, to be selected according to their motivation and academic merit.


L’Institut de Recerca Biomèdica (IRB) Barcelona és un centre d’investigació de renom internacional ubicat al Parc Científic de Barcelona (PCB) i dedicat a entendre qüestions fonamentals sobre la salut i les malalties humanes. L’IRB Barcelona forma part del Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology i els seus objectius inclouen dur a terme una recerca multidisciplinària d’excel·lència en un marc entre la biologia, la química i la medicina, oferint als seus membres, estudiants i visitants una formació d’alt nivel en l’àmbit de les biociències. També ofereix un component d’innovació mitjançant la transferència activa de tecnologia com a benefici envers la societat, així com la participació amb el públic mitjançant activitats de participació i educació. La recerca a l'IRB Barcelona està realitzada per 26 grups que treballen conjuntament amb l'objectiu comú de dur a terme projectes multidisciplinaris que s'ocupen de problemes biomèdics importants que afecten la nostra societat.


L’Institut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE) és un centre de recerca ubicat a la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) que duu a terme una recerca teòrica i experimental de frontera en física fonamental, la qual inclou la física de partícules, l’astrofísica i la cosmologia. Treballa a l’avantguarda de la tecnologia de detecció, per tal de posar els coneixements de la comunitat científica al servei dels objectius més pràctics. L'IFAE participa en el projecte ATLAS de l’LHC, a l’experiment de neutrins T2K del Japó, als telescopis MAGIC de la Palma i al projecte Dark Energy Survey a Xile, entre d’altres. A l'IFAE també es treballa a l'avantguarda de les tecnologies de detecció desenvolupant detectors de píxels per a física d’altes energies, càmeres de telescopis, detectors amb aplicacions mèdiques i altres aplicacions científiques i industrials. El centre compta amb els seus propis investigadors, a més de professors de la UAB i de l’Institut Català de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA), i el personal tècnic.


L'Institut de Ciències Fotòniques (ICFO) és una institució de recerca jove que té com a objectiu fer avançar els límits del coneixement de la fotònica, la ciència i la tecnologia de la llum. La fotònica defineix el camp del coneixement que es dedica a la generació, transmissió, detecció, control i manipulació de la llum, i constitueix una de les tecnologies claus del segle XXI. La llum, concretament la llum làser, és una de les tecnologies més prometedores de què disposa actualment la humanitat. Els seus programes de recerca s'emmarquen en línies de frontera de primer nivell mundial i tenen l'objectiu d'encarar els importants desafiaments als què s'enfronta la societat en general. Es centren en problemes, actuals i de futur, en salut, energia, informació, seguretat, protecció i cura del medi ambient. El paper de les tecnologies fotòniques és ja molt important en una gran diversitat de camps, com ara l'agricultura i el medi ambient, els processos de fabricació i manufactura, els sistemes i serveis de telecomunicacions, la medicina i l'assistència sanitària, les ciències de la vida, la seguretat o l'entreteniment, entre d'altres.


La missió de l'Institut de Ciències de l'Espai (ICE) és contribuir a l'avanç general en els estudis sobre el cosmos, ajudant a millorar la capacitat científica i tecnològica del Consell Superior d'Investigacions Científiques (CSIC), a més de reforçar la presència d'aquesta institució a les iniciatives espacials, promovent l’excel·lència en totes les activitats relacionades amb la investigació científica i la seva divulgació, així com articular la contribució d'aquesta a l'Institut d'Estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC).


L’Institut de Ciència de Materials de Barcelona (ICMAB-CSIC) és un centre d’investigació del Consell Superior d'Investigacions Científiques (CSIC). La seva missió principal és generar nou coneixement en ciència de materials i la seva transferència a la societat, particularment a la indústria europea. Els investigadors del centre caracteritzen els diferents materials i nanomaterials d’interès industrial. L’ICMAB focalitza així la seva activitat en la recerca de frontera en els camps de la ciència dels materials, la nanociència i la nanotecnologia, aconseguint així una integració multidisciplinària de coneixements. L'ICMAB, que compta amb més de 20 anys d'experiència, acull 220 persones amb 57 científics permanents.


L'Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya (IBEC) té com a objectiu dur a terme una recerca de qualitat que, alhora que crea coneixement, contribueixi a una millor qualitat de vida, millori la salut i creï riquesa. L’institut té estrets vincles amb centres de recerca internacionals, universitats i empreses per intercanviar talent i desenvolupar i executar projectes. L’IBEC és un centre de recerca dedicat a la investigació interdisciplinària de primera línia mundial, amb la qual, mitjançant la creació de coneixement, contribueix l’Institut a millorar la salut i la qualitat de vida i a generar riquesa. Entre els beneficiaris de la tasca desenvolupada per l’Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya hi ha les universitats, els centres de recerca, la comunitat científica, el sector empresarial impulsor de la recerca en l’àmbit de la bioenginyeria i la societat en general.


L'Institut Català de Nanociència i Nanotecnologia (ICN2) és un centre d'investigació de reconegut prestigi amb seu a la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB). Les seves línies de recerca se centren en les propietats físiques i químiques recentment descobertes que sorgeixen del fascinant comportament de la matèria a nanoescala. La missió de l’ICN2 és assolir l'excel·lència científica i tecnològica en nanociència i nanotecnologia, i facilitar l'adopció i integració de nanotecnologies en la societat i la indústria. Els patrons de l’ICN2 són la Generalitat de Catalunya, el Consell Superior d'Investigacions Científiques (CSIC) i la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB). L'Institut promou la col·laboració entre científics de diversa formació (física, química, biologia, o enginyeria) per desenvolupar una investigació bàsica i aplicada, perseguint sempre la interacció amb la indústria local i global. L’ICN2 també forma a investigadors en nanotecnologia, du a terme nombroses activitats per facilitar l'adopció de la nanotecnologia per part de la indústria i promou el treball conjunt entre científics, enginyers, tècnics, el món dels negocis, la societat i la política.


L’Institut Català d'Investigació Química (ICIQ) té com a finalitat promoure i desenvolupar una investigació de qualitat en química. Té com a objectius la producció, promoció i divulgació de coneixements i la formació de personal tècnic i científic en química, així com la transferència de tecnologia a la indústria, facilitant el contacte entre investigació bàsica i aplicada i l’establiment de col·laboracions entre l’ICIQ i les empreses.


British Antarctic Survey (BAS) is a component of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC), a world-leading center for polar science and polar operations. Its skilled science and support staff based in Cambridge, Antarctica and the Arctic, work together to deliver research that uses the polar regions to advance our understanding of Earth as a sustainable planet. Through its extensive logistic capability and know how BAS facilitates access for the British and international science community to the UK polar research operation. Numerous national and international collaborations, combined with an excellent infrastructure help sustain a world leading position for the UK in Antarctic affairs.